
Turbocharger VS Supercharger: Which is Better

Turbochargers and superchargers are distinct forced induction systems with differing working principles and applications, providing options for varied performance needs.
When it comes to boosting the performance of your vehicle, two powerful forces are at play – turbochargers and superchargers. The world of automotive engineering has long been enamored with these forced induction systems, each offering unique advantages and characteristics that can turn a stock engine into a powerhouse of horsepower.
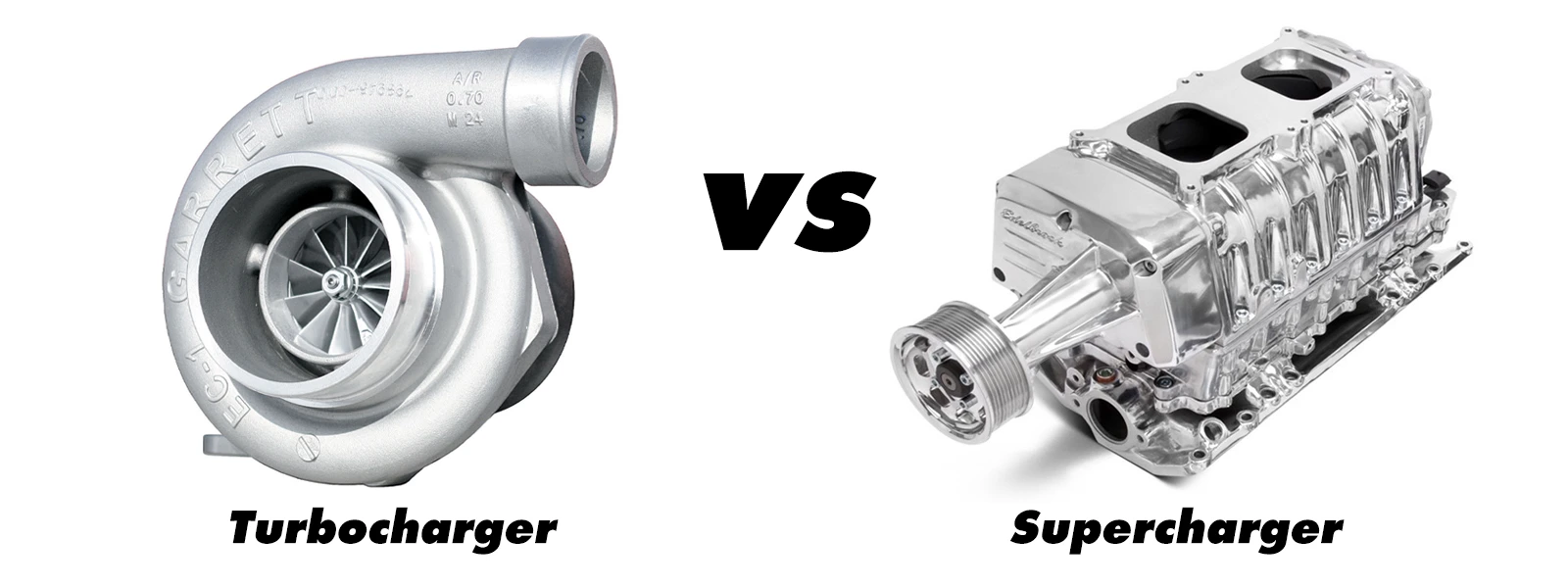
As you stand at the crossroads of power and efficiency, the choice between a turbocharger and a supercharger can be overwhelming. Should you opt for the instant power delivery of a supercharger or embrace the turbo's lag, which often rewards you with an explosive surge? Before delving into their distinctions, it might help to understand their links through the forced induction.
Function of induction
Forced induction is a technology used in automotive and mechanical engineering to increase the power and efficiency of an engine. The fundamental idea behind forced induction is to provide the engine with more oxygen for combustion. When more oxygen is available, it allows for a greater amount of fuel to be burned, leading to a more powerful and efficient combustion process. This, in turn, increases the engine's power output and torque. Turbochargers and superchargers are two main types of forced induction systems.
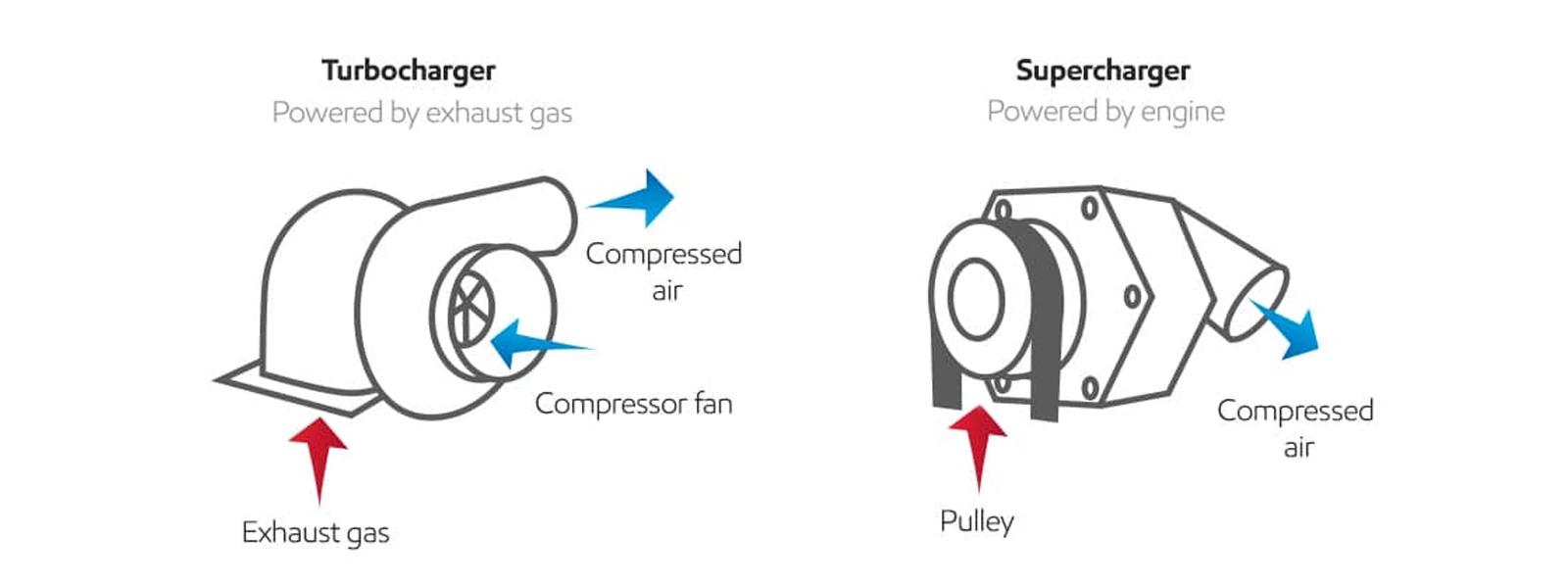
What's the difference between a turbocharger and a supercharger?
-
Power source
Power source
The primary distinction between turbochargers and superchargers lies in their power origins.source. Turbochargers are powered by the engine's exhaust gases, utilizing a turbine connected to the exhaust manifold to drive a compressor. In contrast, superchargers are mechanically driven by the engine's crankshaft, linked via a belt. This fundamental difference in power sources distinguishes the two systems.
-
Power delivery
Power delivery
Turbochargers are often associated with a brief delay in power delivery known as "turbo lag." This delay is due to the need for exhaust gases to reach a certain level to spin the turbine and generate boost. Superchargers, on the other hand, provide immediate and consistent power delivery, making them particularly effective at lower engine speeds.
-
Efficiency
Efficiency
Turbochargers are renowned for their efficiency, as they harness exhaust energy that would otherwise go to waste. This efficiency makes them a preferred choice for maintaining fuel economy under steady-state conditions. In contrast, superchargers consume more fuel because they draw power directly from the engine, potentially leading to reduced fuel efficiency.
-
Installation and complexity
Installation and complexity
Turbocharger installations tend to be more complex, often requiring additional components such as intercoolers and plumbing. Both the exhaust and intake systems may need modification to accommodate the turbocharger. Superchargers are comparatively easier to install and require fewer modifications to the existing vehicle systems.
-
Application
Application
Turbochargers find widespread use in various vehicles, including smaller engines, diesel engines, and applications where fuel efficiency is a priority. Superchargers, on the other hand, are commonly preferred in high-performance and sports cars, racing scenarios, and situations where instant power delivery is essential.
Why are turbos more popular than superchargers?
While superchargers are favored for their immediate power delivery and find applications in high-performance and racing scenarios, turbochargers are the more prevalent choice in the broader automotive market due to:
- Efficiency: Turbochargers are more efficient as they utilize exhaust energy to compress air, improving engine efficiency and fuel economy.
- Emissions Compliance: Turbochargers help reduce emissions by enhancing combustion efficiency, making them a preferred choice to meet stricter emissions regulations.
- Fuel Economy: Turbochargers often lead to better fuel economy during regular driving conditions, aligning with the demand for more environmentally friendly and fuel-efficient vehicles.
- Versatility: Turbochargers can be applied to a wide range of engine sizes and types, from small four-cylinder engines to larger ones, making them suitable for various vehicle applications.
- Performance Potential: Turbochargers can provide substantial power boosts when tuned or modified, making them popular in the high-performance automotive market.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Turbochargers are typically more cost-effective to manufacture and install, potentially resulting in more affordable vehicles for consumers.
- Adaptation to Downsizing: Turbochargers play a crucial role in downsizing engine displacement to maintain performance levels while improving fuel efficiency.
- Global Trend: Turbocharging is a global trend in the automotive industry as it helps meet fuel efficiency and emission standards without sacrificing performance.
Is it feasible to add a turbo or supercharger to my car?
Adding a turbocharger or supercharger to your vehicle is a common aftermarket modification. There are aftermarket kits for both, but consider these key factors before proceeding:
- Compatibility: Ensure your vehicle can accommodate forced induction, as not all are suitable.
- Engine strength: Make sure your engine can handle the added stress and heat.
- Tuning: Precise tuning and calibration are essential for optimal performance.
- Supporting mods: You may need additional modifications like intercoolers or fuel system upgrades.
- Legal compliance: Check local laws and emissions regulations as modifications may impact compliance.
Consult with a professional mechanic or tuner experienced in forced induction systems for guidance. And A-Premium.com is happy to help you by providing the top quality turbos at the most competitive prices!











