What is a car brake master cylinder and what does it do?
A car brake master cylinder plays an important role in the overall balance of the braking system. It is designed to provide equal pressure to all four wheels, which helps ensure that the vehicle stops in a straight line and doesn't pull to one side or the other. It is a hydraulic pump that converts the force applied to the brake pedal by the driver into hydraulic pressure.
Brake master cylinder functions brake master cylinder functions
The main function of the brake master cylinder is to convert the force applied on the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure that is used to actuate the brakes.
When the brake pedal is depressed, it pushes a piston inside the master cylinder which in turn pressurizes the brake fluid in the cylinder. This pressure is then transmitted through the brake lines to the individual brake calipers or wheel cylinders, which then apply the brake pads or shoes to the rotors or drums respectively.
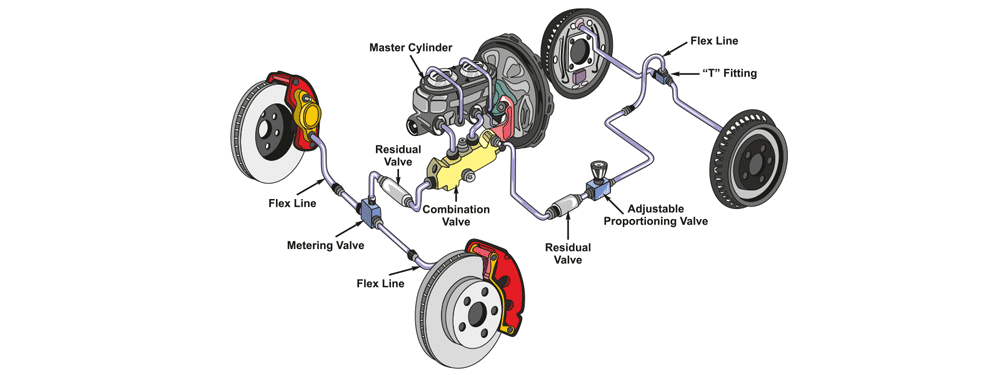
Brake master cylinder diagram
The master cylinder also has two fluid chambers, one for the front brakes and one for the rear brakes, to ensure that the brakes operate independently in case of a leak or failure. It also has a reservoir that holds extra brake fluid and allows for topping up the fluid as needed.
 Master brake cylinder failure symptoms
Master brake cylinder failure symptoms
A failing master brake cylinder can cause a range of symptoms that affect the braking performance of a vehicle. So if you notice the following signs, you may need a new master brake cylinder:
- Brake pedal goes to the floor: If the brake pedal goes all the way to the floor with little resistance, it may indicate a problem with the master brake cylinder. This can be caused by a loss of hydraulic pressure or a problem with the seals inside the master cylinder.
- Brake pedal feels hard: On the other hand, a brake pedal that feels unusually hard or difficult to press down can also indicate a problem with the master brake cylinder. This can be caused by a restriction in the brake lines or a problem with the master cylinder's internal components.
- Brakes are grabbing or dragging: A failing master brake cylinder can cause the brakes to grab or drag, even when the pedal is not pressed. This can result in reduced fuel economy and increased wear on the brake components.
- Noisy brakes: A faulty master brake cylinder can cause the brakes to make unusual noises, such as squeaking, squealing, or grinding. This can indicate that the brake pads or rotors are worn, or that there is a problem with the brake calipers.
- A brake warning light is on: A failing master brake cylinder can cause the brake warning light to come on. This can indicate a problem with the brake system, such as a leak or a loss of hydraulic pressure.
Brake master cylinder replacement steps
Before replacing the brake master cylinder, you need to gather all the necessary tools and equipment. You will need a set of wrenches, pliers, a brake bleeding kit, a container to catch brake fluid, and a new brake master cylinder. After that, follow the steps:
- Disconnect the brake lines and wiring harness from the old master cylinder.
- Remove the old master cylinder by unscrewing the bolts that secure it to the brake booster.
- Install the new master cylinder onto the brake booster and tighten the bolts.
- Reconnect the brake lines and wiring harness to the new master cylinder.
- Use a brake bleeding kit to bleed the brake lines and remove any air bubbles from the system.
- Test the brake pedal to ensure that it feels firm and responsive.
- Adjust the pushrod that connects the brake booster to the master cylinder, if necessary.
- Check the brake fluid level in the reservoir and top it off if necessary, and you’re recommended to use the type of brake fluid recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.












