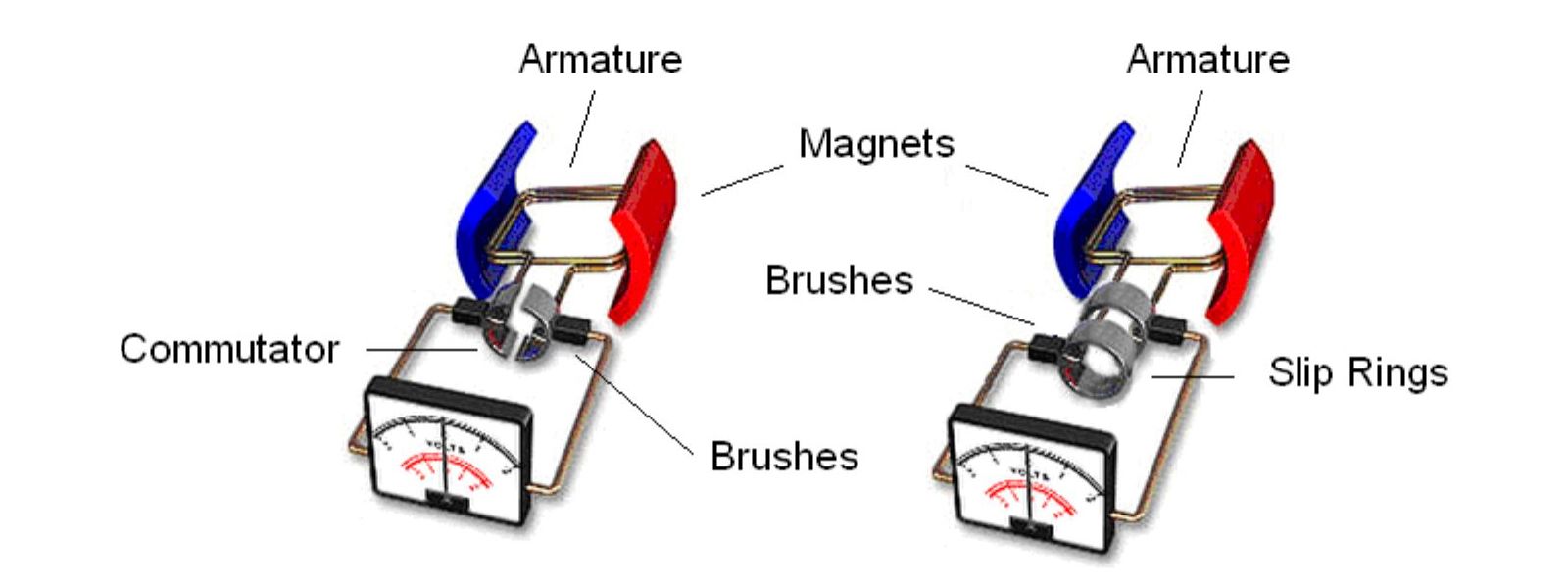
Difference Between Generator And Alternator
Although generators and alternators are both used to generate electricity, they differ significantly in their construction, function, and the type of electrical current they produce. This blog will introduce you to the differences between the two.
While the two terms generator and alternator are often used interchangeably, they are not one and the same. Understanding the difference between a car generator and an alternator is essential for effective maintenance, troubleshooting, and upgrading of the vehicle's electrical system. It enables accurate diagnosis of problems, ensures compatibility when replacing components, and allows for informed decisions during customization. Knowledge of the distinction also helps optimize battery charging, prevents overcharging or undercharging, and extends battery lifespan.
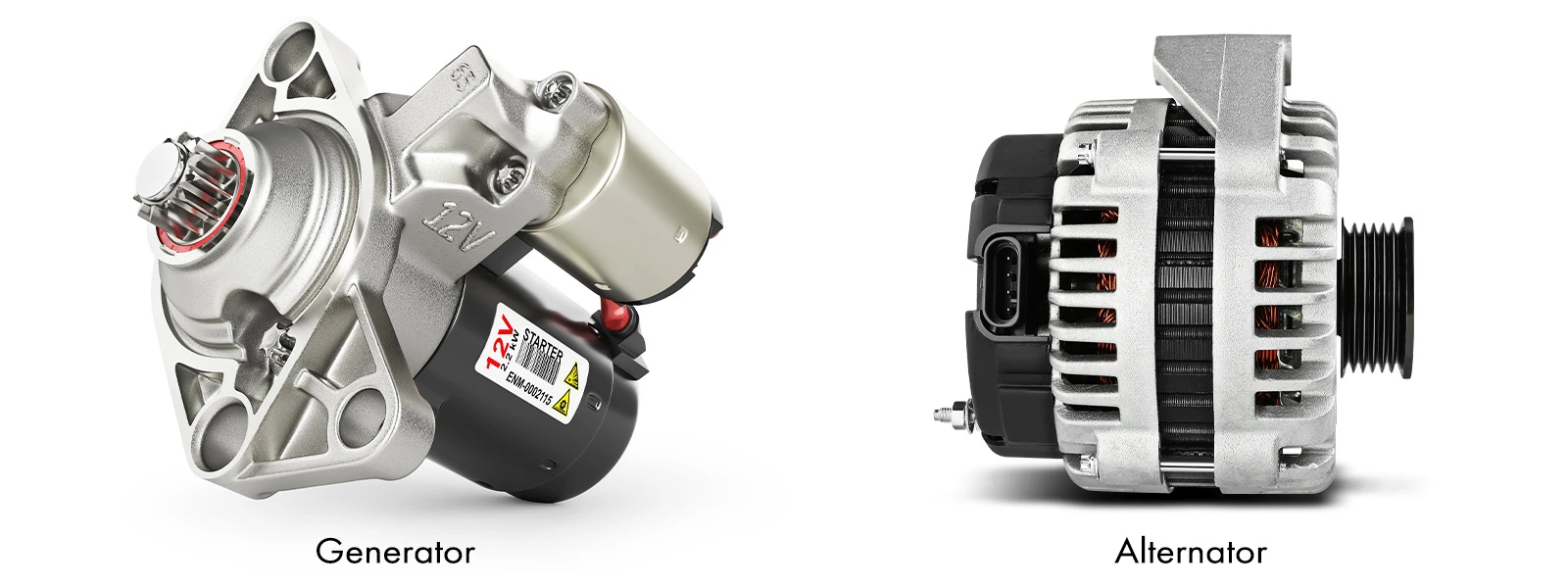

Prior to delving into the specific disparities, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of the definition and functioning of both the generator and alternator. To put it simply, an alternator is responsible for generating electrical power using a rotating magnetic field and converting it from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC). A generator, however, serves as a mechanical device that transforms mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy. Its primary function is to charge the battery and supply power to the electrical components of the vehicle.
The main differences between an alternator and a generator
The main differences between the alternator and generator exist in the following points.
1. Power Conversion: A generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. It relies on the principles of Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction. The alternator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction. It also relies on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction.
2. Power Output: The generator can produce both AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) power depending on the design and configuration. The alternator primarily produces alternating current, although some modern alternators can also produce direct current by rectifying the AC output.
3. Excitation: Generator excitation can be achieved by a variety of methods, such as permanent magnets, excitation coils or external power sources. The alternator requires an external DC power supply to establish the initial magnetic field for excitation. Once the initial field is established, it can generate its own excitation power.
4. Voltage Regulation: Generators usually require manual regulation of voltage by adjusting speed or load. Some generators may have an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) to maintain a stable voltage output. The alternator is generally equipped with an automatic voltage regulator (AVR), which monitors the output voltage and adjusts the excitation to maintain a stable voltage output.
5. Applications: Generators are often used as backup power sources, portable generators, or in remote areas with limited grid access. Alternators are widely used in automotive applications, power plants, industrial machinery, and as the primary source of power for residential, commercial, and utility facilities.
6. Complexity: Generators are usually simpler in design, with fewer components and a simple structure. The alternator is usually more complex because it contains additional components such as slip rings, brushes, and voltage regulators.
7. Efficiency: Generator efficiency may vary depending on design, size and operating conditions. The alternator is known for its high efficiency due to advancements in design and technology. They can achieve higher energy conversion rates compared to generators.
8. Size and Weight: The generator is relatively large and heavy, making it less portable and suitable for fixed installations. The alternator is compact and lightweight, making it more portable and suitable for mobile or temporary power applications.
9. Starting Ability: A generator may require an external device such as a starter motor or battery to start the power generation process. The alternator is self-starting without any external assistance, and the initial excitation is achieved through an external DC power supply.
10. Operating Speed: The generator operates at a constant speed regardless of electrical load, resulting in fuel consumption even during periods of low demand. The alternator operates at variable speeds depending on the electrical load, thereby improving fuel efficiency and reducing noise levels.
11. Cost: Generators are generally less expensive than alternators, especially for smaller power ratings. Alternators are generally more expensive than generators because they are more efficient and require additional components.
12. Maintenance: Generators require regular maintenance, including oil changes, spark plug replacements and regular inspections. Alternators generally require less maintenance due to the absence of brushes and commutators, resulting in less wear and tear. However, regular inspection and maintenance of the AVR and other components is still necessary.
Alternator vs generator, the FAQs
Question 1: What is the main difference between a car generator and an alternator?
Answer: The main difference lies in the type of current they produce and their design. Car generators produce direct current (DC), while car alternators generate alternating current (AC) that is then converted to DC using a rectifier.
Question 2: What are the advantages of a car alternator over a generator?
Answer: Car alternators have several advantages over generators, including:
- Compact size and lightweight design.
- High efficiency in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Ability to charge the battery while simultaneously powering the car's electrical systems.
- Regulation of output voltage to maintain a consistent charge level.

Question 3: Can a car alternator be used as a generator?
Answer: In some cases, a car alternator can be used as a generator with modifications. However, it's important to note that car alternators are not designed for standalone operation, and using them as generators may require additional components and adjustments to ensure proper voltage regulation and compatibility with the load.
Question 4: Which type of current, AC or DC, is used in most modern cars?
Answer: Most modern cars use direct current (DC) for their electrical systems. The alternating current (AC) generated by the car alternator is converted to DC using a rectifier before being used to charge the battery and power the car's electrical components.
Question 5: Are car generators still used in modern vehicles?
Answer: Car generators are not commonly used in modern vehicles. They were used in older vehicle models and have been largely replaced by alternators due to their efficiency and other advantages.