What Does a Car Alternator Do
Car alternators are essential for powering a vehicle's electrical components and recharging the battery by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Read this blog to maintain your vehicle's electrical system and avoid problems.
Although you might assume that your car battery supplies electricity for all the electrical components in your vehicle, such as the headlights, windshield wipers, and radio, the truth is that the car alternator is primarily responsible for generating most of the electricity. The charging system in a gasoline- or diesel-powered car consists of three key elements: the battery, the voltage regulator, and an alternator. The alternator collaborates with the battery to produce electricity for various electrical components in the vehicle, including the interior and exterior lights, as well as the instrument panel. The term "alternator" is derived from "alternating current" (AC), indicating its function of generating this type of electrical current.
The alternator is typically located near the engine in a car. It is commonly positioned on the side of the engine, driven by a belt connected to the crankshaft pulley. The exact location can vary depending on the make and model of the vehicle, but it is often found at the front of the engine compartment. In some cars, it may be more accessible from underneath the vehicle. It is connected to the engine and electrical system through various wires and cables.
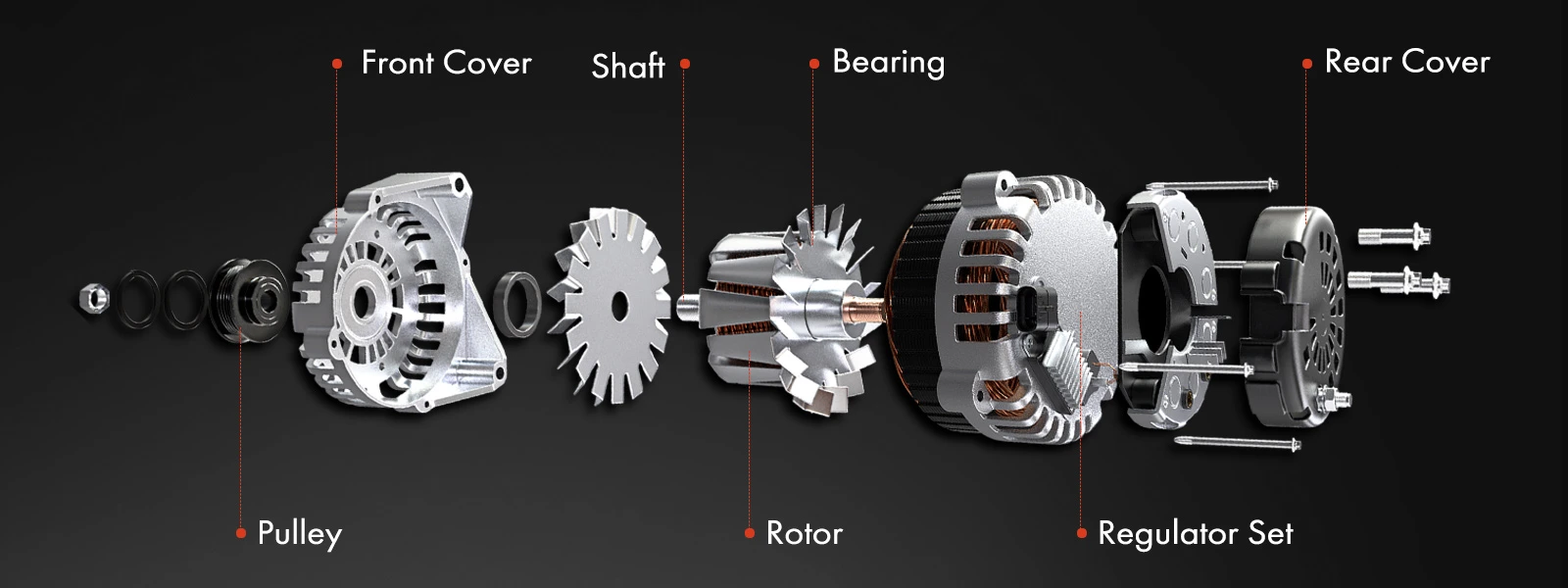
Components of an alternator
In general, alternators are compact and lightweight components. They are typically about the size of a coconut. In passenger cars, light trucks, and even most hybrids, the alternators are designed with outer housing made of aluminum. This choice of material is significant because aluminum does not retain magnetism. It is crucial because the production of electrical power within the alternator generates substantial heat, and aluminum effectively dissipates this heat. Additionally, the rotor assembly of the alternator creates a magnetic field.
- Stator and Rotor
Stator: The stator consists of a stationary set of wire coils that surround the rotor. These coils are connected to the vehicle's electrical system and provide the necessary magnetic field for power generation.
Rotor: The rotor is the rotating part of the alternator. It is usually composed of a coil or magnet that spins within the stator's magnetic field when the engine is running. The movement of the rotor induces an electrical current in the stator windings.
- Diode Rectifier: The diode rectifier is responsible for converting the alternating current (AC) produced by the alternator into direct current (DC). It consists of a set of diodes that allow current flow in one direction, ensuring a consistent flow of electrical power.
- Voltage Regulator: The voltage regulator regulates the electrical output of the alternator to maintain a steady voltage level. It monitors the system's electrical needs and adjusts the current supplied to the rotor, controlling the output voltage.
- Cooling System: Alternators have a cooling system to dissipate the heat generated during operation. It typically includes a fan, cooling fins, or a dedicated cooling circuit to prevent overheating and maintain optimal performance.
How does an alternator work?
When the engine is running, the rotation of the crankshaft causes the rotor inside the alternator to spin. This spinning rotor creates a magnetic field around it. The stator, consisting of wire coils, surrounds the rotor. As the rotor spins, it induces an alternating current (AC) in the stator windings due to the changing magnetic field.
The AC produced in the stator windings is then converted into direct current (DC) using a rectifier. The rectifier is a set of diodes that allow the current to flow in one direction, effectively converting the AC into DC. This rectified DC is the type of electrical current that most automotive systems require to function.
However, the voltage output of the alternator can vary depending on the engine speed and the electrical load. To regulate the voltage and ensure it remains within the desired range, an alternator also incorporates a voltage regulator. The voltage regulator monitors the electrical system's voltage and adjusts the rotor's magnetic field strength accordingly to control the output voltage.
Additionally, the alternator has a pulley and a belt connected to the engine's crankshaft. The rotational motion of the crankshaft is transferred to the alternator's rotor through this mechanical connection. The belt-driven system allows the alternator to generate electricity as long as the engine is running. The electrical energy produced by the alternator is distributed to various components within the vehicle. It powers the headlights, taillights, interior lights, audio system, and other electrical accessories. Simultaneously, any excess electrical energy generated by the alternator is used to recharge the vehicle's battery.
Common failures of a car alternator
Like other components in our vehicles, alternators are susceptible to failure. They contain moving parts that can accumulate dirt and are exposed to the stresses caused by temperature fluctuations. Consequently, the internal components gradually deteriorate over time. Common alternator failures may include:
- Bearing failure: Worn-out or damaged bearings cause noise, vibration, and eventual alternator failure.
- Diode failure: Failed diodes lead to AC ripple, battery drain, and inconsistent charging.
- Voltage regulator failure: A faulty voltage regulator results in overcharging or undercharging, damaging the battery and causing electrical issues.
- The stator or rotor failure: Faulty stator windings or rotor assembly cause reduced power generation or complete alternator failure.
- Belt slippage or tensioner failure: Loose, worn, or broken belts prevent alternator rotation, leading to charging loss.
- Wiring or connection issues: Faulty wiring, loose connections, or corroded terminals disrupt the electrical flow, impacting alternator performance.
- Overheating: Excessive electrical load, inadequate cooling, or poor ventilation causes overheating, leading to internal component degradation.
- Water damage: Exposure to water/moisture leads to corrosion, short circuits, and component failure.
- Age and wear: Natural wear and tear over time result in decreased performance or failure.
How to protect your car alternator
Alternator maintenance is crucial for the overall health and performance of the vehicle's electrical system. By following a few key steps, you can ensure that your alternator remains in good working condition:
- Periodically check for damage, loose connections, and worn-out belts.
- Regularly clean the alternator and surrounding area to remove dirt and debris.
- Ensure the alternator belt is properly tensioned.
- Check battery terminals for corrosion and keep them charged.
- Minimize using power-hungry accessories simultaneously.
- Attend to any electrical problems promptly to prevent strain on the alternator.







