How to Check Your Alternator

It’s crucial to master the art of checking your car’s alternator, and this blog will guide you on how to check your generator. With simple inspection steps, you can detect and resolve generator problems promptly.
Suggested A-Premium Parts
The alternator charges the battery and other electrical components while the car is running. A bad alternator can cause problems such as weak lights and a vehicle engine that won't start. Therefore, it is very important to check the alternator of your car regularly. This blog will introduce you to the method of checking the alternator.
What Does an Alternator Do
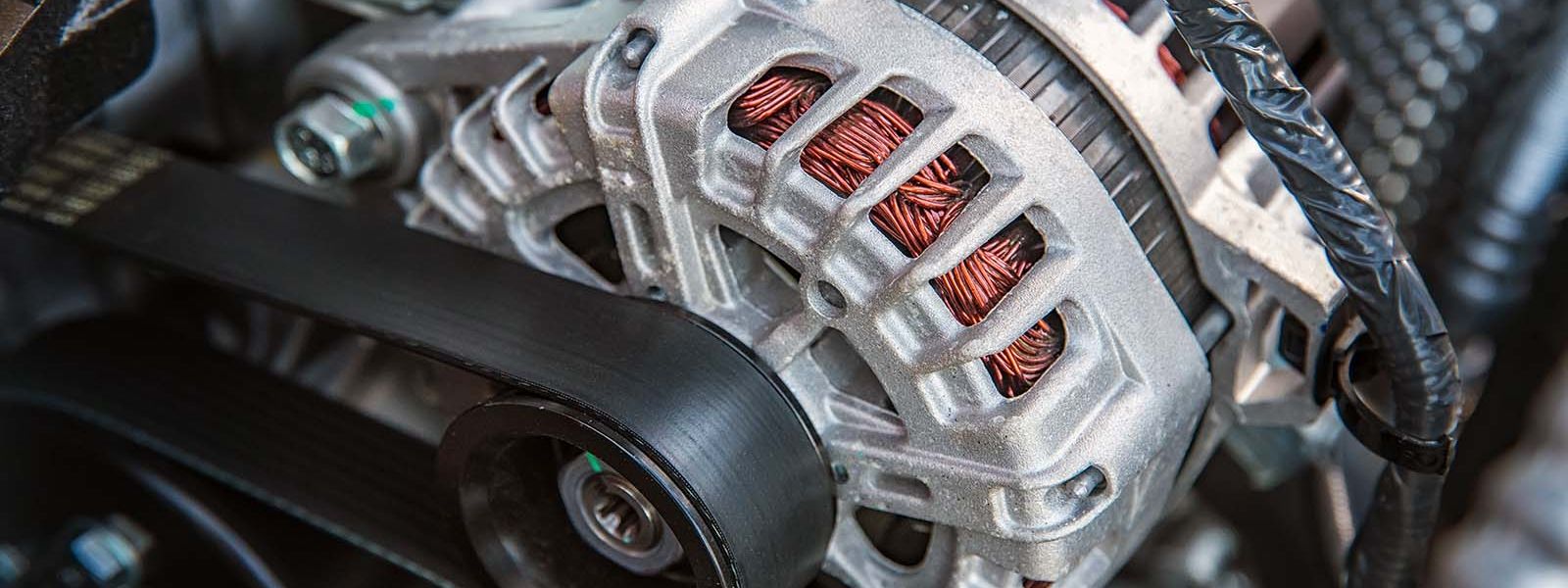
An alternator, often called a synchronous generator (shown below), is a device designed to produce alternating current power at a specific frequency. It uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to generate electricity using a coil wrapped around an iron core. These coils can generate electricity in two main ways:
The coil is rotated in a stationary magnetic field.
The magnetic field is caused to rotate around a fixed coil.
The alternator mainly uses the second power generation method. Its two core components are:
- Rotor: A magnetic field is generated by a direct current (DC) power supply, which in turn excites the rotor coil. The rotor rotates driven by a prime mover, such as a car engine. This rotation causes the magnetic flux generated by the rotor to rotate at the same speed as the rotor.
- Armature Coil: This part is stationary. The rotating magnetic flux in the rotor induces a current in the armature coils.
Alternators are particularly common in automobiles, where they are used to charge the battery while driving. In addition, this technology is also widely used in various traditional energy power generation platforms. Such as nuclear power plants, natural gas power plants, thermal power plants and hydropower plants, etc.
Alternator Malfunction Symptoms
If the car won't start, even if the battery is in good condition, the alternator may be faulty. When your alternator is having problems or performing poorly, the following common signs may appear:
- Battery light on the dashboard: This is one of the most common signs that the alternator is failing.
- Starting the engine slowly or not starting at all: Since the alternator is responsible for charging the battery if the alternator fails, the battery may not get enough power to start the engine.
- Decreased performance of vehicle electrical components: The alternator provides power to various electrical components in your vehicle, including the headlights, battery, and interior lights. If the alternator is not performing well, these electrical components may show signs of reduced performance.
- Alternator Making Unusual Sounds: If there is a problem within the alternator, it may make a rumbling or other unusual sound.
- Burning smell: A burning smell may occur when there is an electrical issue within the alternator. This smell is usually caused by short wires, overheating, or other electrical problems.
- Vehicle Won't Jump Start: If you try to jump-start the failed vehicle using another vehicle and the vehicle still won't start, the problem may be with the alternator.
If you have the above symptoms, you should immediately send the car to a professional repair shop for maintenance. Timely detection and repair of generator faults can prevent greater damage to the power system and ensure safe driving of the car.
Car Battery Voltage
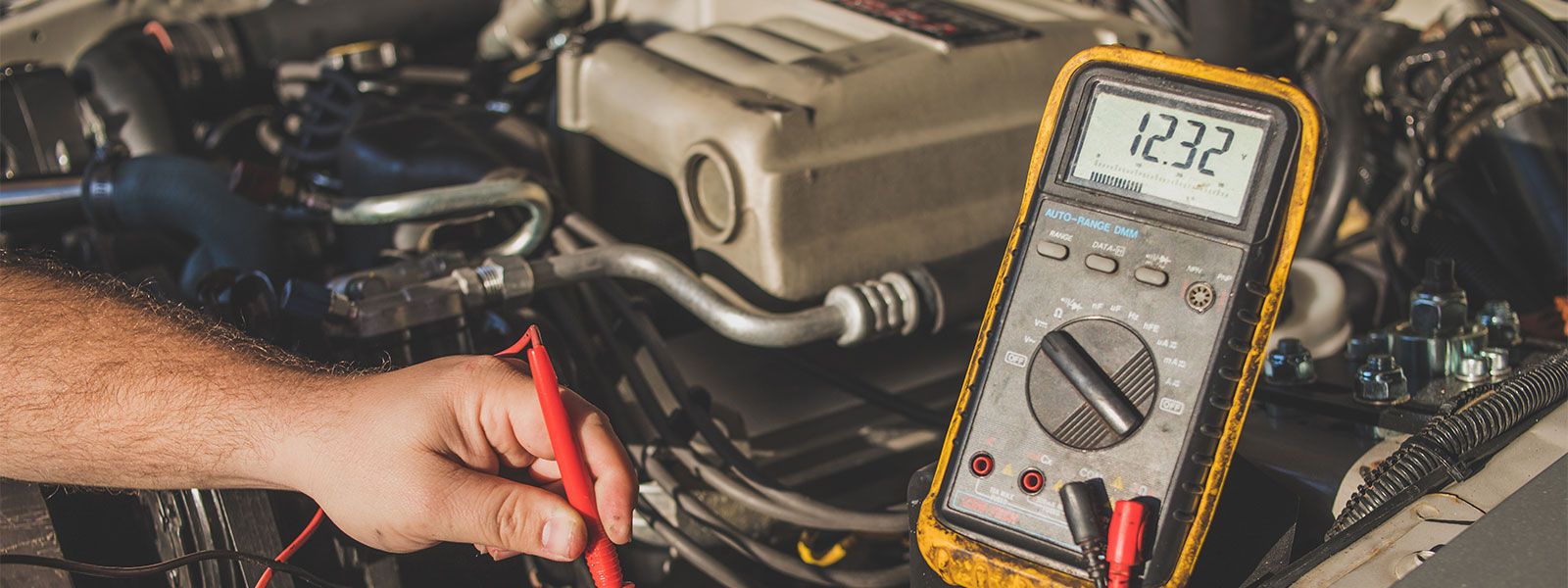
In most cases, the quiescent voltage of a car battery will remain in the range of 12.4 to 12.6 volts. However, when the alternator starts feeding power through the vehicle's internal wiring system, the voltage it produces decreases due to resistance in the transmission of current. To compensate for this voltage loss, the alternator will increase the output voltage accordingly, usually settling at around 14.5 volts.
The measured car battery voltage will vary from vehicle to vehicle due to possible voltage drops in the wiring system while the vehicle is being driven. But no matter what, the battery voltage in operation is always higher than the voltage in its resting state. Typically, when all the vehicle's electrical accessories are turned off, the voltage of the car battery will be close to or slightly above 14 volts.
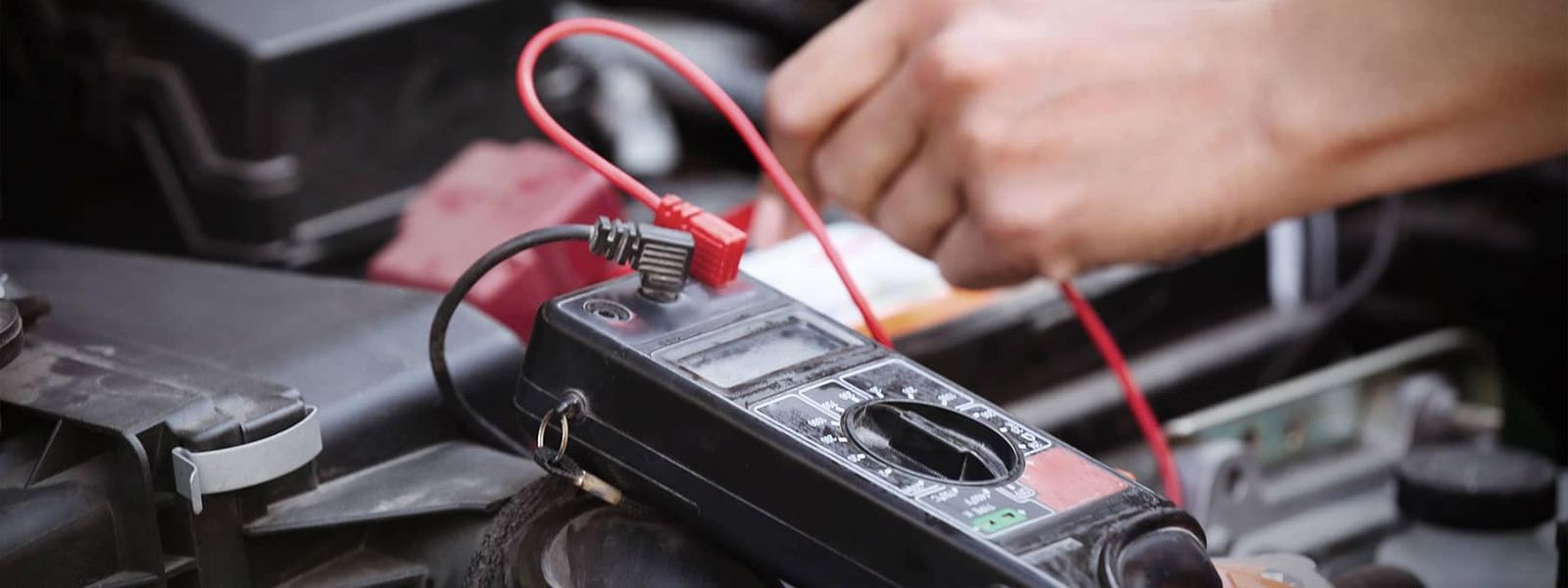
How Do You Test An Alternator With a Voltmeter
Here's how to test your car's alternator using a voltmeter:
- Preliminary preparation: Check whether the car's battery is fully charged. Check the alternator drive belt tension to make sure it is in proper condition. Turn off the ignition switch and disconnect the battery ground wire harness to ensure safety.
- Connect a voltmeter: Connect a voltmeter between the alternator's "B" terminal (usually the generator's output) and ground. The positive pen of the voltmeter should be connected to the "B" terminal, and the negative pen should be connected to the ground or negative electrode of the battery.
- Carry out a preliminary test: turn on the ignition switch and check whether the voltmeter voltage is equal to the battery voltage. If the reading is 0V, there is an open circuit between the alternator "B" terminal and the battery and battery negative terminal.
- Start the engine: Start the engine and turn off all lights and electrical equipment switches.
- Read the voltage value: When the alternator output current drops below 10A, read the voltmeter reading.
- Judgment result: If the voltmeter reading is consistent with the standard value, the alternator is working properly. If the voltmeter reading does not match the standard value, the alternator may be faulty.
In addition, if the vehicle is equipped with other electronic devices, such as a charging indicator light or voltage regulator, you can also observe the status of these devices to help determine the working condition of the alternator.
When the alternator is tested, the safe operation procedure must be followed to ensure the stability and safety of the vehicle. If the use method is not clear, can consult a professional vehicle maintenance technician.
FAQs
Q: What voltage should an alternator test at?
A: 13.5 - 14.5 volts
Q: What tools can you use to check your car's alternator?
A: There are many tools that can be used to check the car’s alternator, including but not limited to the following: multimeter, voltmeter, ammeter and oscilloscope. In addition, you can also use some simple tools such as a light bulb or a small homemade test light. etc., by changing the working state of the car to observe changes in the brightness of the light bulb, thereby indirectly judging the working condition of the generator.
The importance of regular maintenance of the alternator to the car cannot be ignored. It is directly related to the normal operation of the vehicle and the safety of the driver. As an important part of a vehicle's electrical system, the alternator is responsible for charging the vehicle's battery and providing the power needed by various electrical devices and systems. When the alternator fails, it will cause an insufficient or interrupted power supply, making the car unable to drive normally. In severe cases, it may cause the vehicle to stall or malfunction. Regular maintenance of the alternator and timely troubleshooting can ensure that the motor works in optimal condition and reduce maintenance costs.